Getting started with DIPY¶
In diffusion MRI (dMRI) usually we use three types of files, a Nifti file with the diffusion weighted data, and two text files one with b-values and one with the b-vectors.
In DIPY we provide tools to load and process these files and we also provide access to publicly available datasets for those who haven’t acquired yet their own datasets.
With the following commands we can download a dMRI dataset
from dipy.data import fetch_sherbrooke_3shell
fetch_sherbrooke_3shell()
By default these datasets will go in the .dipy folder inside your home directory.
Here is how you can access them.
from os.path import expanduser, join
home = expanduser('~')
dname holds the directory name where the 3 files are in.
dname = join(home, '.dipy', 'sherbrooke_3shell')
Here, we show the complete filenames of the 3 files
fdwi = join(dname, 'HARDI193.nii.gz')
print(fdwi)
fbval = join(dname, 'HARDI193.bval')
print(fbval)
fbvec = join(dname, 'HARDI193.bvec')
print(fbvec)
/home/username/.dipy/sherbrooke_3shell/HARDI193.nii.gz
/home/username/.dipy/sherbrooke_3shell/HARDI193.bval
/home/username/.dipy/sherbrooke_3shell/HARDI193.bvec
Now, that we have their filenames we can start checking what these look like.
Let’s start first by loading the dMRI datasets. For this purpose, we use a python library called nibabel which enables us to read and write neuroimaging-specific file formats.
import nibabel as nib
img = nib.load(fdwi)
data = img.get_data()
data is a 4D array where the first 3 dimensions are the i, j, k voxel
coordinates and the last dimension is the number of non-weighted (S0s) and
diffusion-weighted volumes.
We can very easily check the size of data in the following way:
print(data.shape)
(128, 128, 60, 193)
We can also check the dimensions of each voxel in the following way:
print(img.header.get_zooms()[:3])
(2.0, 2.0, 2.0)
We can quickly visualize the results using matplotlib. For example, let’s show here the middle axial slices of volume 0 and volume 10.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
axial_middle = data.shape[2] // 2
plt.figure('Showing the datasets')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1).set_axis_off()
plt.imshow(data[:, :, axial_middle, 0].T, cmap='gray', origin='lower')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2).set_axis_off()
plt.imshow(data[:, :, axial_middle, 10].T, cmap='gray', origin='lower')
plt.show()
plt.savefig('data.png', bbox_inches='tight')
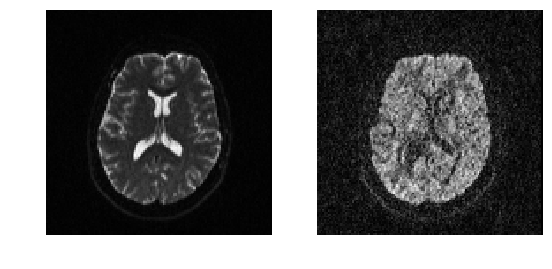
Showing the middle axial slice without (left) and with (right) diffusion weighting.¶
The next step is to load the b-values and b-vectors from the disk using
the function read_bvals_bvecs.
from dipy.io import read_bvals_bvecs
bvals, bvecs = read_bvals_bvecs(fbval, fbvec)
In DIPY, we use an object called GradientTable which holds all the
acquisition specific parameters, e.g. b-values, b-vectors, timings and others.
To create this object you can use the function gradient_table.
from dipy.core.gradients import gradient_table
gtab = gradient_table(bvals, bvecs)
Finally, you can use gtab (the GradientTable object) to show some information about the
acquisition parameters
print(gtab.info)
- B-values shape (193,)
min 0.000000 max 3500.000000
- B-vectors shape (193, 3)
min -0.964050 max 0.999992
You can also see the b-values using:
print(gtab.bvals)
[ 0. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000.
1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000.
1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000.
1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000.
1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000.
1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000.
1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 1000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000.
2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000.
2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000.
2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000.
2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000.
2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000.
2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 2000. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500. 3500.
3500. 3500. 3500.]
Or, for example the 10 first b-vectors using:
print(gtab.bvecs[:10, :])
array([[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0.999979 , -0.00504001, -0.00402795],
[ 0. , 0.999992 , -0.00398794],
[-0.0257055 , 0.653861 , -0.756178 ],
[ 0.589518 , -0.769236 , -0.246462 ],
[-0.235785 , -0.529095 , -0.815147 ],
[-0.893578 , -0.263559 , -0.363394 ],
[ 0.79784 , 0.133726 , -0.587851 ],
[ 0.232937 , 0.931884 , -0.278087 ],
[ 0.93672 , 0.144139 , -0.31903 ]])
gtab can be used to tell what part of the data is the S0 volumes
(volumes which correspond to b-values of 0).
S0s = data[:, :, :, gtab.b0s_mask]
Here, we had only 1 S0 as we can verify by looking at the dimensions of S0s
print(S0s.shape)
(128, 128, 60, 1)
Just, for fun let’s save this in a new Nifti file.
nib.save(nib.Nifti1Image(S0s, img.affine), 'HARDI193_S0.nii.gz')
Now, that we learned how to load dMRI datasets we can start the analysis. See example Reconstruction of the diffusion signal with the Tensor model to learn how to create FA maps.
Example source code
You can download the full source code of this example. This same script is also included in the dipy source distribution under the doc/examples/ directory.