Using Various Stopping Criterion for Tractography¶
The stopping criterion determines if the tracking stops or continues at each tracking position. The tracking stops when it reaches an ending region (e.g. low FA, gray matter or corticospinal fluid regions) or exits the image boundaries. The tracking also stops if the direction getter has no direction to follow.
Each stopping criterion determines if the stopping is ‘valid’ or ‘invalid’. A streamline is ‘valid’ when the stopping criterion determines if the streamline stops in a position classified as ‘ENDPOINT’ or ‘OUTSIDEIMAGE’. A streamline is ‘invalid’ when it stops in a position classified as ‘TRACKPOINT’ or ‘INVALIDPOINT’. These conditions are described below. The ‘LocalTracking’ generator can be set to output all generated streamlines or only the ‘valid’ ones. See Girard et al. (2004) [Girard2014] and Smith et al.(2012) [Smith2012] for more details on these methods.
This example is an extension of the An introduction to the Deterministic Maximum Direction Getter example. We begin by loading the data, creating a seeding mask from white matter voxels of the corpus callosum, fitting a Constrained Spherical Deconvolution (CSD) reconstruction model and creating the maximum deterministic direction getter.
# Enables/disables interactive visualization
interactive = False
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from dipy.data import (read_stanford_labels,
default_sphere,
read_stanford_pve_maps)
from dipy.direction import DeterministicMaximumDirectionGetter
from dipy.io.streamline import save_trk
from dipy.io.stateful_tractogram import Space, StatefulTractogram
from dipy.reconst.csdeconv import (ConstrainedSphericalDeconvModel,
auto_response)
from dipy.reconst.dti import fractional_anisotropy, TensorModel
from dipy.tracking import utils
from dipy.tracking.local_tracking import LocalTracking
from dipy.tracking.streamline import Streamlines
from dipy.tracking.stopping_criterion import (ActStoppingCriterion,
BinaryStoppingCriterion,
ThresholdStoppingCriterion)
from dipy.viz import window, actor, colormap, has_fury
hardi_img, gtab, labels_img = read_stanford_labels()
_, _, img_pve_wm = read_stanford_pve_maps()
data = hardi_img.get_data()
labels = labels_img.get_data()
affine = hardi_img.affine
white_matter = img_pve_wm.get_data()
seed_mask = (labels == 2)
seed_mask[img_pve_wm.get_data() < 0.5] = 0
seeds = utils.seeds_from_mask(seed_mask, affine, density=2)
response, ratio = auto_response(gtab, data, roi_radius=10, fa_thr=0.7)
csd_model = ConstrainedSphericalDeconvModel(gtab, response)
csd_fit = csd_model.fit(data, mask=white_matter)
dg = DeterministicMaximumDirectionGetter.from_shcoeff(csd_fit.shm_coeff,
max_angle=30.,
sphere=default_sphere)
Threshold Stopping Criterion¶
A scalar map can be used to define where the tracking stops. The threshold stopping criterion uses a scalar map to stop the tracking whenever the interpolated scalar value is lower than a fixed threshold. Here, we show an example using the fractional anisotropy (FA) map of the DTI model. The threshold stopping criterion uses a trilinear interpolation at the tracking position.
Parameters
metric_map: numpy array [:, :, :]
threshold: float
Stopping States
‘ENDPOINT’: stops at a position where metric_map < threshold; the streamline
reached the target stopping area. - ‘OUTSIDEIMAGE’: stops at a position outside of metric_map; the streamline reached an area outside the image where no direction data is available. - ‘TRACKPOINT’: stops at a position because no direction is available; the streamline is stopping where metric_map >= threshold, but there is no valid direction to follow. - ‘INVALIDPOINT’: N/A.
tensor_model = TensorModel(gtab)
tenfit = tensor_model.fit(data, mask=labels > 0)
FA = fractional_anisotropy(tenfit.evals)
threshold_criterion = ThresholdStoppingCriterion(FA, .2)
fig = plt.figure()
mask_fa = FA.copy()
mask_fa[mask_fa < 0.2] = 0
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(mask_fa[:, :, data.shape[2] // 2].T, cmap='gray', origin='lower',
interpolation='nearest')
fig.tight_layout()
fig.savefig('threshold_fa.png')
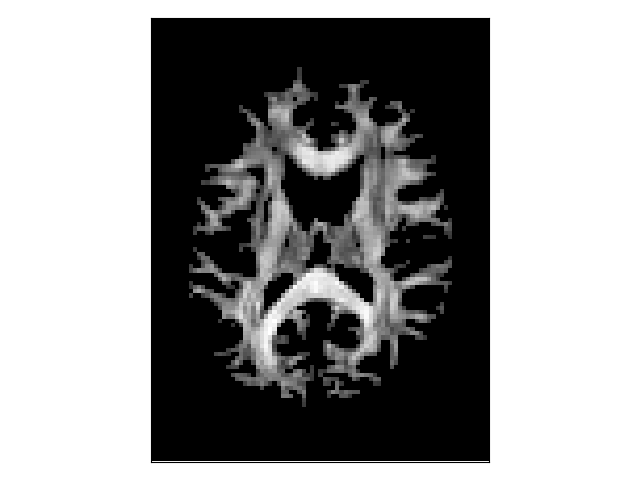
Thresholded fractional anisotropy map.¶
streamline_generator = LocalTracking(dg,
threshold_criterion,
seeds,
affine,
step_size=.5,
return_all=True)
streamlines = Streamlines(streamline_generator)
sft = StatefulTractogram(streamlines, hardi_img, Space.RASMM)
save_trk(sft, "tractogram_probabilistic_thresh_all.trk")
if has_fury:
r = window.Renderer()
r.add(actor.line(streamlines, colormap.line_colors(streamlines)))
window.record(r, out_path='tractogram_deterministic_thresh_all.png',
size=(800, 800))
if interactive:
window.show(r)
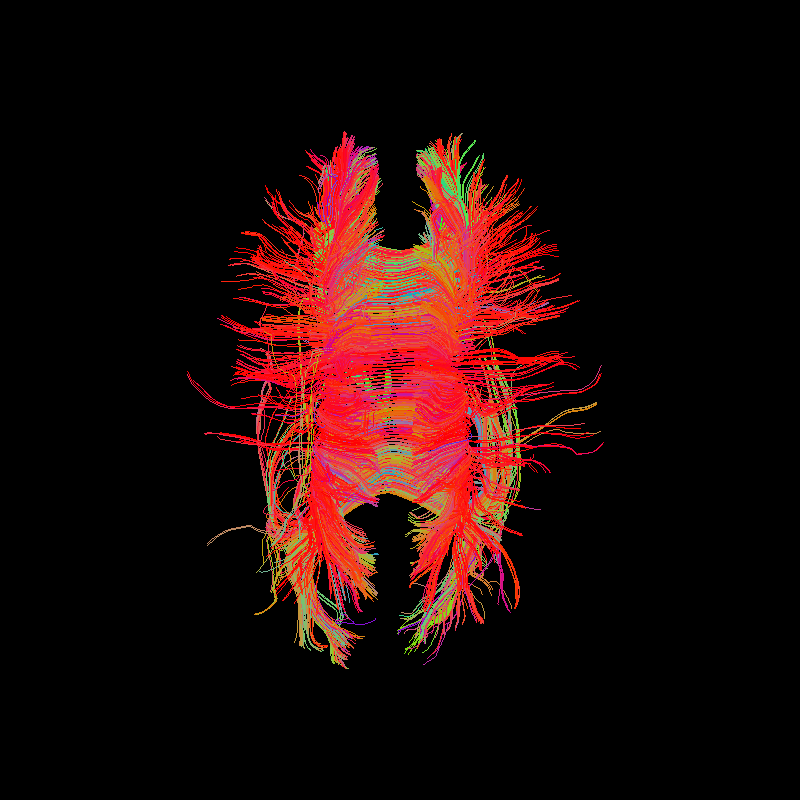
Corpus Callosum using deterministic tractography with a thresholded fractional anisotropy mask.¶
Binary Stopping Criterion¶
A binary mask can be used to define where the tracking stops. The binary stopping criterion stops the tracking whenever the tracking position is outside the mask. Here, we show how to obtain the binary stopping criterion from the white matter mask defined above. The binary stopping criterion uses a nearest-neighborhood interpolation at the tracking position.
Parameters
mask: numpy array [:, :, :]
Stopping States
‘ENDPOINT’: stops at a position where mask = 0; the streamline
reached the target stopping area. - ‘OUTSIDEIMAGE’: stops at a position outside of metric_map; the streamline reached an area outside the image where no direction data is available. - ‘TRACKPOINT’: stops at a position because no direction is available; the streamline is stopping where mask > 0, but there is no valid direction to follow. - ‘INVALIDPOINT’: N/A.
binary_criterion = BinaryStoppingCriterion(white_matter == 1)
fig = plt.figure()
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
fig.tight_layout()
plt.imshow(white_matter[:, :, data.shape[2] // 2].T, cmap='gray',
origin='lower', interpolation='nearest')
fig.savefig('white_matter_mask.png')
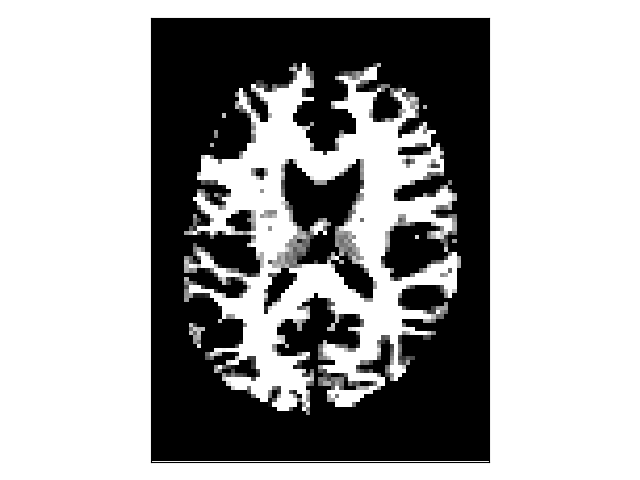
White matter binary mask.¶
streamline_generator = LocalTracking(dg,
binary_criterion,
seeds,
affine,
step_size=.5,
return_all=True)
streamlines = Streamlines(streamline_generator)
sft = StatefulTractogram(streamlines, hardi_img, Space.RASMM)
save_trk(sft, "tractogram_deterministic_binary_all.trk")
if has_fury:
r = window.Renderer()
r.add(actor.line(streamlines, colormap.line_colors(streamlines)))
window.record(r, out_path='tractogram_deterministic_binary_all.png',
size=(800, 800))
if interactive:
window.show(r)
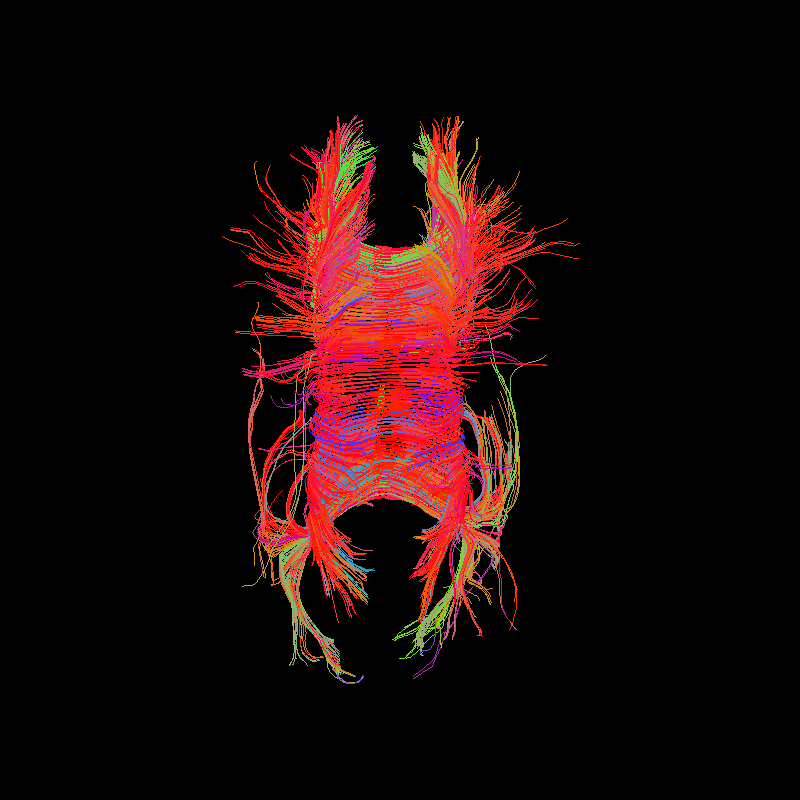
Corpus Callosum using deterministic tractography with a binary white matter mask.¶
ACT Stopping Criterion¶
Anatomically-constrained tractography (ACT) [Smith2012] uses information from
anatomical images to determine when the tractography stops. The include_map
defines when the streamline reached a ‘valid’ stopping region (e.g. gray
matter partial volume estimation (PVE) map) and the exclude_map defines
when the streamline reached an ‘invalid’ stopping region (e.g. corticospinal
fluid PVE map). The background of the anatomical image should be added to the
include_map to keep streamlines exiting the brain (e.g. through the
brain stem). The ACT stopping criterion uses a trilinear interpolation
at the tracking position.
Parameters
include_map: numpy array[:, :, :],exclude_map: numpy array[:, :, :],
Stopping States
‘ENDPOINT’: stops at a position where
include_map> 0.5; the streamline
reached the target stopping area.
- ‘OUTSIDEIMAGE’: stops at a position outside of include_map or
exclude_map; the streamline reached an area outside the image where no
direction data is available.
- ‘TRACKPOINT’: stops at a position because no direction is available; the
streamline is stopping where include_map < 0.5 and exclude_map < 0.5,
but there is no valid direction to follow.
- ‘INVALIDPOINT’: exclude_map > 0.5; the streamline reach a position which
is anatomically not plausible.
img_pve_csf, img_pve_gm, img_pve_wm = read_stanford_pve_maps()
background = np.ones(img_pve_gm.shape)
background[(img_pve_gm.get_data() +
img_pve_wm.get_data() +
img_pve_csf.get_data()) > 0] = 0
include_map = img_pve_gm.get_data()
include_map[background > 0] = 1
exclude_map = img_pve_csf.get_data()
act_criterion = ActStoppingCriterion(include_map, exclude_map)
fig = plt.figure()
plt.subplot(121)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(include_map[:, :, data.shape[2] // 2].T, cmap='gray',
origin='lower', interpolation='nearest')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(exclude_map[:, :, data.shape[2] // 2].T, cmap='gray',
origin='lower', interpolation='nearest')
fig.tight_layout()
fig.savefig('act_maps.png')
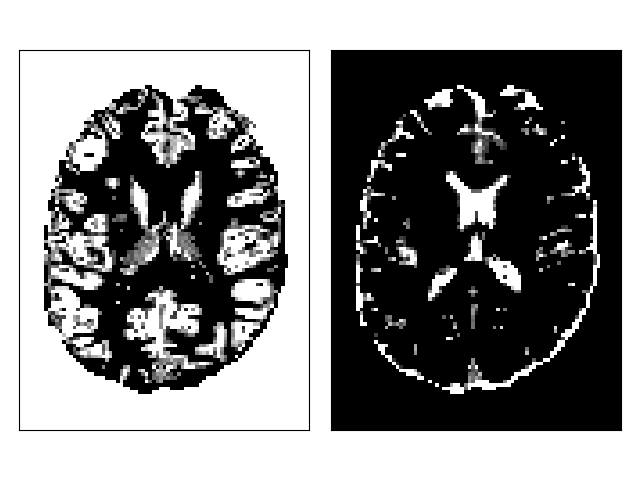
Include (left) and exclude (right) maps for ACT.¶
streamline_generator = LocalTracking(dg,
act_criterion,
seeds,
affine,
step_size=.5,
return_all=True)
streamlines = Streamlines(streamline_generator)
sft = StatefulTractogram(streamlines, hardi_img, Space.RASMM)
save_trk(sft, "tractogram_deterministic_act_all.trk")
if has_fury:
r = window.Renderer()
r.add(actor.line(streamlines, colormap.line_colors(streamlines)))
window.record(r, out_path='tractogram_deterministic_act_all.png',
size=(800, 800))
if interactive:
window.show(r)
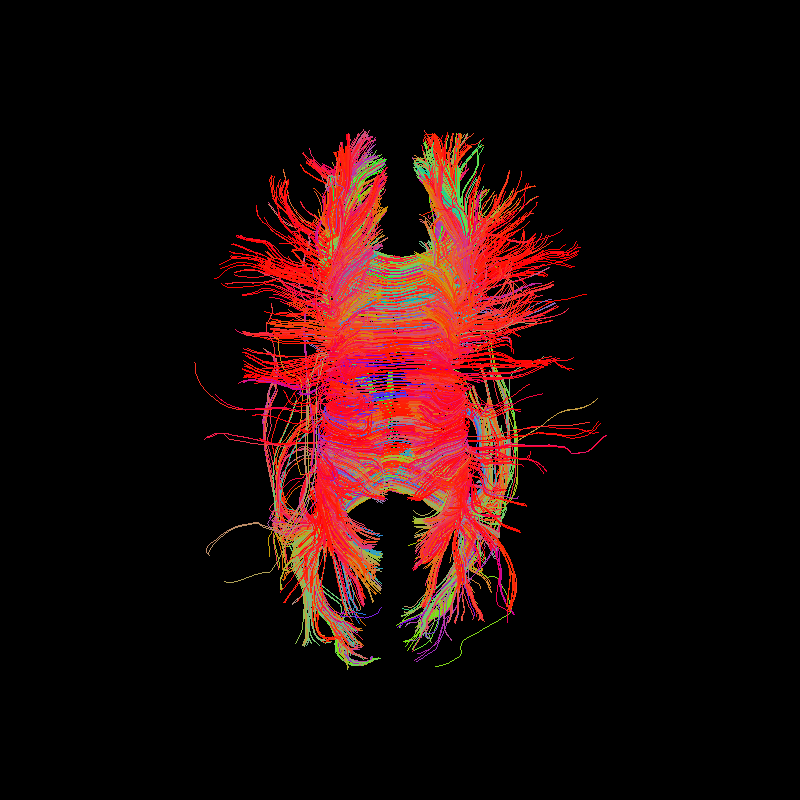
Corpus Callosum using deterministic tractography with ACT stopping criterion.¶
streamline_generator = LocalTracking(dg,
act_criterion,
seeds,
affine,
step_size=.5,
return_all=False)
streamlines = Streamlines(streamline_generator)
sft = StatefulTractogram(streamlines, hardi_img, Space.RASMM)
save_trk(sft, "tractogram_deterministic_act_valid.trk")
if has_fury:
r = window.Renderer()
r.add(actor.line(streamlines, colormap.line_colors(streamlines)))
window.record(r, out_path='tractogram_deterministic_act_valid.png',
size=(800, 800))
if interactive:
window.show(r)
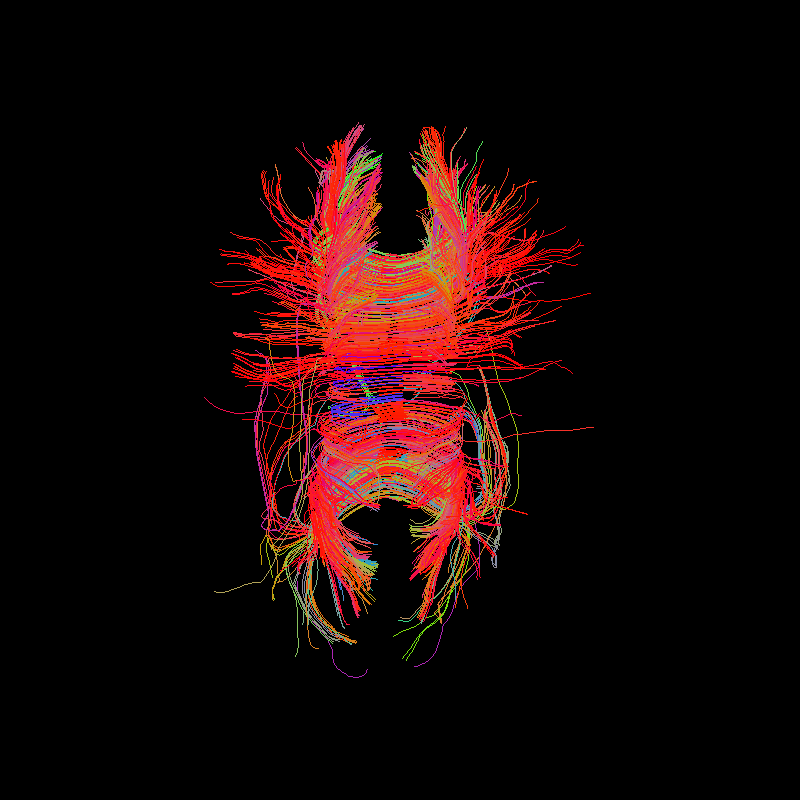

Corpus Callosum using deterministic tractography with ACT stopping criterion. Streamlines ending in gray matter region only.¶
The threshold and binary stopping criterion use respectively a scalar map and a binary mask to stop the tracking. The ACT stopping criterion use partial volume fraction (PVE) maps from an anatomical image to stop the tracking. Additionally, the ACT stopping criterion determines if the tracking stopped in expected regions (e.g. gray matter) and allows the user to get only streamlines stopping in those regions.
Notes¶
Currently,the proposed method that cuts streamlines going through subcortical gray matter regions is not implemented. The backtracking technique for streamlines reaching INVALIDPOINT is not implemented either [Smith2012].
References¶
- Smith2012(1,2,3)
Smith, R. E., Tournier, J.-D., Calamante, F., & Connelly, A. Anatomically-constrained tractography: Improved diffusion MRI streamlines tractography through effective use of anatomical information. NeuroImage, 63(3), 1924-1938, 2012.
- Girard2014
Girard, G., Whittingstall, K., Deriche, R., & Descoteaux, M. Towards quantitative connectivity analysis: reducing tractography biases. NeuroImage, 98, 266-278, 2014.
Example source code
You can download the full source code of this example. This same script is also included in the dipy source distribution under the doc/examples/ directory.