Reconstruction with the Sparse Fascicle Model¶
In this example, we will use the Sparse Fascicle Model (SFM) [Rokem2015], to reconstruct the fiber Orientation Distribution Function (fODF) in every voxel.
First, we import the modules we will use in this example:
import dipy.reconst.sfm as sfm
import dipy.data as dpd
import dipy.direction.peaks as dpp
from dipy.viz import window, actor
For the purpose of this example, we will use the Stanford HARDI dataset (150 directions, single b-value of 2000 \(s/mm^2\)) that can be automatically downloaded. If you have not yet downloaded this data-set in one of the other examples, you will need to be connected to the internet the first time you run this example. The data will be stored for subsequent runs, and for use with other examples.
from dipy.data import read_stanford_hardi
img, gtab = read_stanford_hardi()
data = img.get_data()
# Enables/disables interactive visualization
interactive = False
Reconstruction of the fiber ODF in each voxel guides subsequent tracking steps. Here, the model is the Sparse Fascicle Model, described in [Rokem2014]. This model reconstructs the diffusion signal as a combination of the signals from different fascicles. This model can be written as:
Where \(y\) is the signal and \(\beta\) are weights on different points in the sphere. The columns of the design matrix, \(X\) are the signals in each point in the measurement that would be predicted if there was a fascicle oriented in the direction represented by that column. Typically, the signal used for this kernel will be a prolate tensor with axial diffusivity 3-5 times higher than its radial diffusivity. The exact numbers can also be estimated from examining parts of the brain in which there is known to be only one fascicle (e.g. in corpus callosum).
Sparsity constraints on the fiber ODF (\(\beta\)) are set through the Elastic Net algorihtm [Zou2005].
Elastic Net optimizes the following cost function:
where \(\hat{y}\) is the signal predicted for a particular setting of \(\beta\), such that the left part of this expression is the squared loss function; \(\alpha\) is a parameter that sets the balance between the squared loss on the data, and the regularization constraints. The regularization parameter \(\lambda\) sets the l1_ratio, which controls the balance between L1-sparsity (low sum of weights), and low L2-sparsity (low sum-of-squares of the weights).
Just like Constrained Spherical Deconvolution (see Reconstruction with Constrained Spherical Deconvolution), the SFM
requires the definition of a response function. We’ll take advantage of the
automated algorithm in the csdeconv module to find this response
function:
from dipy.reconst.csdeconv import auto_response
response, ratio = auto_response(gtab, data, roi_radius=10, fa_thr=0.7)
The response return value contains two entries. The first is an array with
the eigenvalues of the response function and the second is the average S0 for
this response.
It is a very good practice to always validate the result of auto_response.
For, this purpose we can print it and have a look at its values.
print(response)
(array([ 0.0014, 0.00029, 0.00029]), 416.206)
We initialize an SFM model object, using these values. We will use the default sphere (362 vertices, symmetrically distributed on the surface of the sphere), as a set of putative fascicle directions that are considered in the model
sphere = dpd.get_sphere()
sf_model = sfm.SparseFascicleModel(gtab, sphere=sphere,
l1_ratio=0.5, alpha=0.001,
response=response[0])
For the purpose of the example, we will consider a small volume of data containing parts of the corpus callosum and of the centrum semiovale
data_small = data[20:50, 55:85, 38:39]
Fitting the model to this small volume of data, we calculate the ODF of this model on the sphere, and plot it.
sf_fit = sf_model.fit(data_small)
sf_odf = sf_fit.odf(sphere)
fodf_spheres = actor.odf_slicer(sf_odf, sphere=sphere, scale=0.8, colormap='plasma')
ren = window.Renderer()
ren.add(fodf_spheres)
print('Saving illustration as sf_odfs.png')
window.record(ren, out_path='sf_odfs.png', size=(1000, 1000))
if interactive:
window.show(ren)
We can extract the peaks from the ODF, and plot these as well
sf_peaks = dpp.peaks_from_model(sf_model,
data_small,
sphere,
relative_peak_threshold=.5,
min_separation_angle=25,
return_sh=False)
window.clear(ren)
fodf_peaks = actor.peak_slicer(sf_peaks.peak_dirs, sf_peaks.peak_values)
ren.add(fodf_peaks)
print('Saving illustration as sf_peaks.png')
window.record(ren, out_path='sf_peaks.png', size=(1000, 1000))
if interactive:
window.show(ren)
Finally, we plot both the peaks and the ODFs, overlayed:
fodf_spheres.GetProperty().SetOpacity(0.4)
ren.add(fodf_spheres)
print('Saving illustration as sf_both.png')
window.record(ren, out_path='sf_both.png', size=(1000, 1000))
if interactive:
window.show(ren)
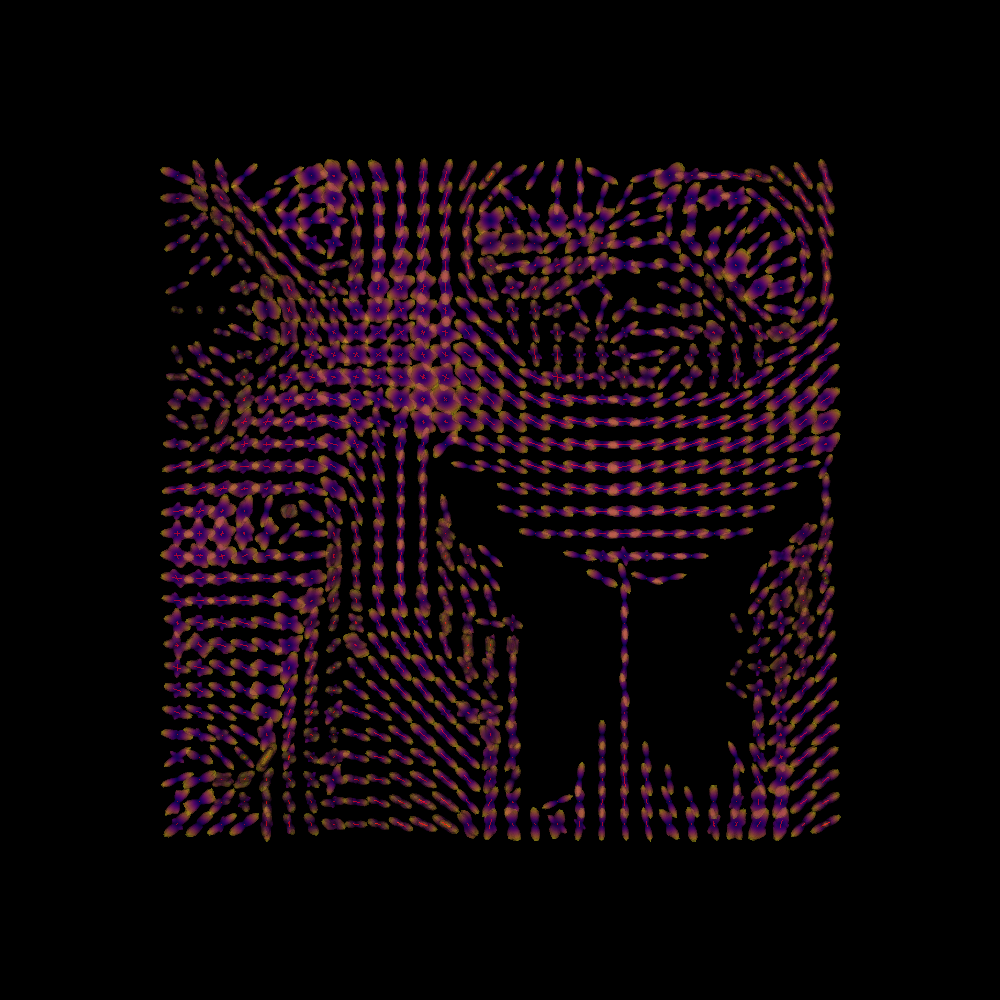
SFM Peaks and ODFs.¶
To see how to use this information in tracking, proceed to Tracking with the Sparse Fascicle Model.
References¶
- Rokem2015
Ariel Rokem, Jason D. Yeatman, Franco Pestilli, Kendrick N. Kay, Aviv Mezer, Stefan van der Walt, Brian A. Wandell (2015). Evaluating the accuracy of diffusion MRI models in white matter. PLoS ONE 10(4): e0123272. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123272
- Zou2005
Zou H, Hastie T (2005). Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc B:301-320
Example source code
You can download the full source code of this example. This same script is also included in the dipy source distribution under the doc/examples/ directory.