Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Fast Streamline Search#
This example explains how Fast Streamline Search [StOnge2022] can be used to find all similar streamlines.
First import the necessary modules.
import numpy as np
from dipy.data import (get_target_tractogram_hcp, get_two_hcp842_bundles,
fetch_bundle_atlas_hcp842, fetch_target_tractogram_hcp)
from dipy.io.streamline import load_trk
from dipy.segment.fss import FastStreamlineSearch, nearest_from_matrix_row
from dipy.viz import actor, window
Download and read data for this tutorial
fetch_bundle_atlas_hcp842()
fetch_target_tractogram_hcp()
hcp_file = get_target_tractogram_hcp()
streamlines = load_trk(hcp_file, "same", bbox_valid_check=False).streamlines
Visualize the atlas (ref) bundle and full brain tractogram
interactive = False
scene = window.Scene()
scene.SetBackground(1, 1, 1)
scene.add(actor.line(streamlines))
if interactive:
window.show(scene)
else:
window.record(scene, out_path='tractograms_initial.png', size=(600, 600))
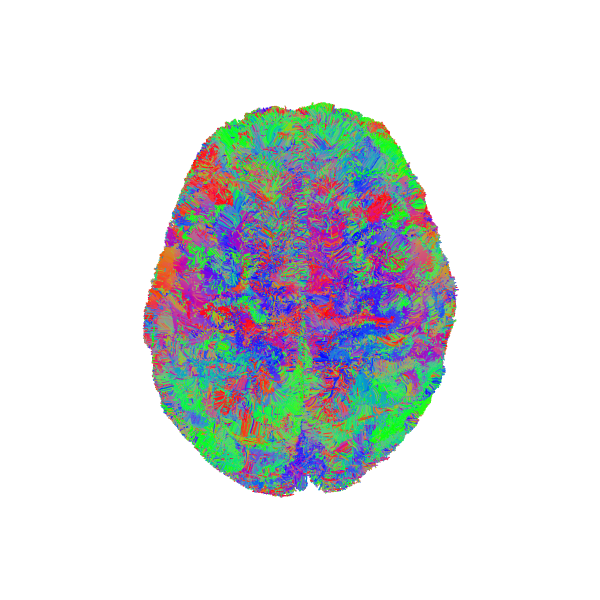
Atlas bundle and source streamlines before registration.
Read Arcuate Fasciculus Left and Corticospinal Tract Left bundles from already fetched atlas data to use them as model bundle. Let’s visualize the Arcuate Fasciculus Left model bundle.
model_af_l_file, model_cst_l_file = get_two_hcp842_bundles()
sft_af_l = load_trk(model_af_l_file, "same", bbox_valid_check=False)
model_af_l = sft_af_l.streamlines
scene = window.Scene()
scene.SetBackground(1, 1, 1)
scene.add(actor.line(model_af_l, colors=(0, 1, 0)))
scene.set_camera(focal_point=(-18.17281532, -19.55606842, 6.92485857),
position=(-360.11, -30.46, -40.44),
view_up=(-0.03, 0.028, 0.89))
if interactive:
window.show(scene)
else:
window.record(scene, out_path='AF_L_model_bundle.png',
size=(600, 600))
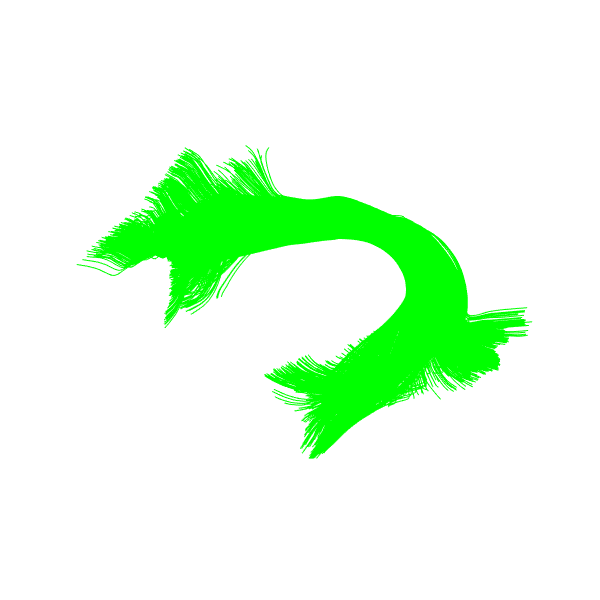
Model Arcuate Fasciculus Left bundle
Search for all similar streamlines [StOnge2022]
Fast Streamline Search can do a radius search to find all streamlines that are similar to from one tractogram to another. It returns the distance matrix mapping between both tractograms. The same list of streamlines can be given to recover the self distance matrix.
here are the FastStreamlinesSearch class need the following
initialization arguments:
ref_streamlines : reference streamlines, that will be searched in (tree)
max_radius : is the maximum distance that can be used with radius search
Then, the radius_search() method needs the following arguments:
- radius : for each streamline search find all similar ones in the
“ref_streamlines” that are within the given radius
Be cautious, a large radius might result in a dense distance computation, requiring a large amount of time and memory. Recommended range of the radius is from 1 to 10 mm.
radius = 7.0
fs_tree_af = FastStreamlineSearch(ref_streamlines=model_af_l,
max_radius=radius)
coo_mdist_mtx = fs_tree_af.radius_search(streamlines, radius=radius)
Extract indices of streamlines with an similar ones in the reference
ids_s = np.unique(coo_mdist_mtx.row)
ids_ref = np.unique(coo_mdist_mtx.col)
recognized_af_l = streamlines[ids_s].copy()
let’s visualize streamlines similar to the Arcuate Fasciculus Left bundle
scene = window.Scene()
scene.SetBackground(1, 1, 1)
scene.add(actor.line(recognized_af_l, colors=(0, 0, 1)))
scene.set_camera(focal_point=(-18.17281532, -19.55606842, 6.92485857),
position=(-360.11, -30.46, -40.44),
view_up=(-0.03, 0.028, 0.89))
if interactive:
window.show(scene)
else:
window.record(scene, out_path='AF_L_recognized_bundle.png',
size=(600, 600))
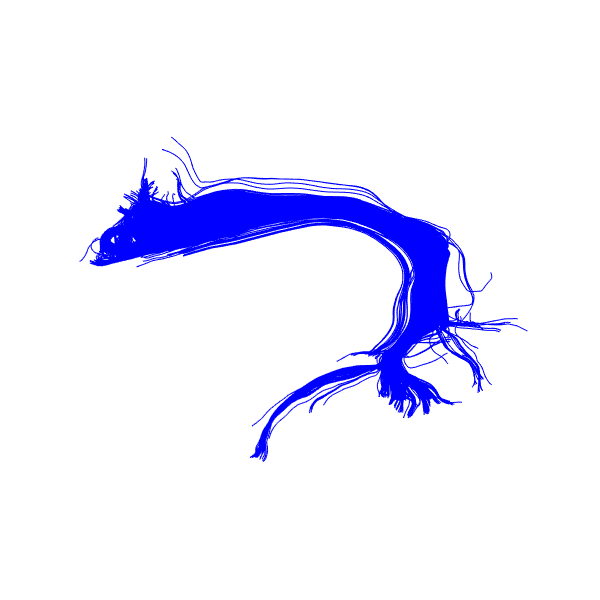

Recognized Arcuate Fasciculus Left bundle
Color the resulting AF by the nearest streamlines distance
nn_s, nn_ref, nn_dist = nearest_from_matrix_row(coo_mdist_mtx)
scene = window.Scene()
scene.SetBackground(1, 1, 1)
cmap = actor.colormap_lookup_table(scale_range=(nn_dist.min(), nn_dist.max()))
scene.add(actor.line(recognized_af_l, colors=nn_dist, lookup_colormap=cmap))
scene.add(actor.scalar_bar(cmap, title="distance to atlas (mm)"))
scene.set_camera(focal_point=(-18.17281532, -19.55606842, 6.92485857),
position=(-360.11, -30.46, -40.44),
view_up=(-0.03, 0.028, 0.89))
if interactive:
window.show(scene)
else:
window.record(scene, out_path='AF_L_recognized_bundle_dist.png',
size=(600, 600))
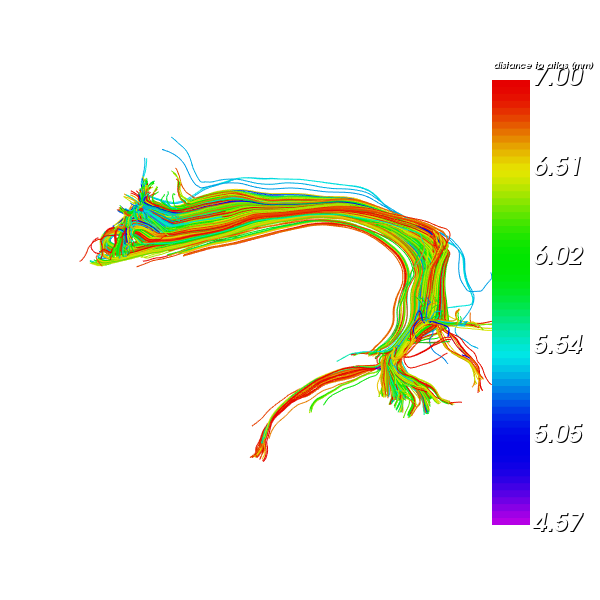
Recognized Arcuate Fasciculus Left bundle colored by distance to ref
Display the streamlines reference reached in green
# Default red color
ref_color = np.zeros((len(model_af_l), 3), dtype=float)
ref_color[:] = (1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
# Reached in green color
ref_color[ids_ref] = (0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
scene = window.Scene()
scene.SetBackground(1, 1, 1)
scene.add(actor.line(model_af_l, ref_color))
scene.set_camera(focal_point=(-18.17281532, -19.55606842, 6.92485857),
position=(-360.11, -30.46, -40.44),
view_up=(-0.03, 0.028, 0.89))
if interactive:
window.show(scene)
else:
window.record(scene, out_path='AF_L_model_bundle_reached.png',
size=(600, 600))
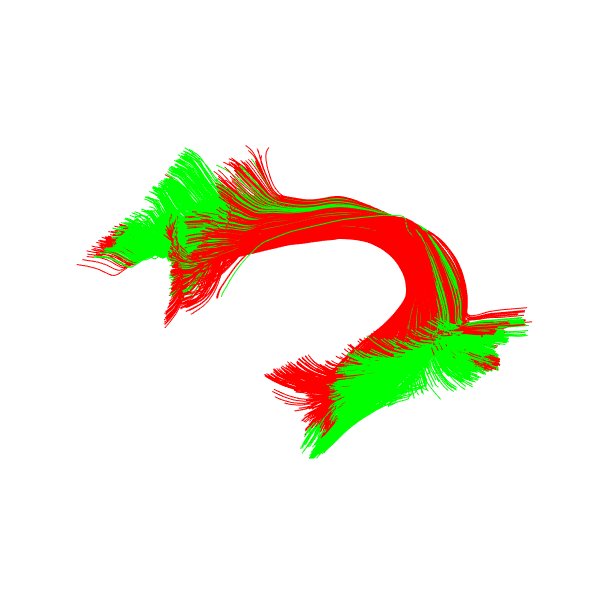
Arcuate Fasciculus Left model reached (green) in radius
References#
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 41.102 seconds)