Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Brain segmentation with median_otsu#
We show how to extract brain information and mask from a b0 image using DIPY’s
segment.mask module.
First import the necessary modules:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from dipy.core.histeq import histeq
from dipy.data import get_fnames
from dipy.io.image import load_nifti, save_nifti
from dipy.segment.mask import median_otsu
Download and read the data for this tutorial.
The scil_b0 dataset contains different data from different companies and
models. For this example, the data comes from a 1.5 Tesla Siemens MRI.
data_fnames = get_fnames(name="scil_b0")
data, affine = load_nifti(data_fnames[1])
data = np.squeeze(data)
Segment the brain using DIPY’s mask module.
median_otsu returns the segmented brain data and a binary mask of the
brain. It is possible to fine tune the parameters of median_otsu
(median_radius and num_pass) if extraction yields incorrect results
but the default parameters work well on most volumes. For this example,
we used 2 as median_radius and 1 as num_pass
b0_mask, mask = median_otsu(data, median_radius=2, numpass=1)
Saving the segmentation results is very easy. We need the b0_mask, and
the binary mask volumes. The affine matrix which transform the image’s
coordinates to the world coordinates is also needed. Here, we choose to save
both images in float32.
fname = "se_1.5t"
save_nifti(fname + "_binary_mask.nii.gz", mask.astype(np.float32), affine)
save_nifti(fname + "_mask.nii.gz", b0_mask.astype(np.float32), affine)
Quick view of the results middle slice using matplotlib.
sli = data.shape[2] // 2
plt.figure("Brain segmentation")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1).set_axis_off()
plt.imshow(histeq(data[:, :, sli].astype("float")).T, cmap="gray", origin="lower")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2).set_axis_off()
plt.imshow(histeq(b0_mask[:, :, sli].astype("float")).T, cmap="gray", origin="lower")
plt.savefig(f"{fname}_median_otsu.png", bbox_inches="tight")
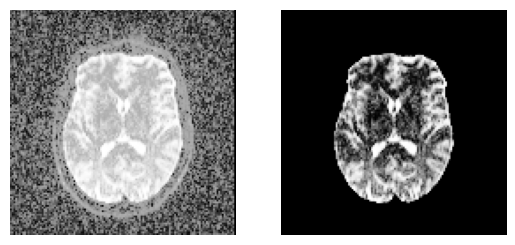
An application of median_otsu for brain segmentation.
median_otsu can also automatically crop the outputs to remove the largest
possible number of background voxels. This makes outputted data significantly
smaller. Auto-cropping in median_otsu is activated by setting the
autocrop parameter to True.
b0_mask_crop, mask_crop = median_otsu(data, median_radius=4, numpass=4, autocrop=True)
Saving cropped data as demonstrated previously.
save_nifti(fname + "_binary_mask_crop.nii.gz", mask_crop.astype(np.float32), affine)
save_nifti(fname + "_mask_crop.nii.gz", b0_mask_crop.astype(np.float32), affine)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 16.826 seconds)