Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Calculate SHORE scalar maps#
We show how to calculate two SHORE-based scalar maps: return to origin probability (RTOP) [1] and mean square displacement (MSD) [2], [3] on your data. SHORE can be used with any multiple b-value dataset like multi-shell or DSI.
First import the necessary modules:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from dipy.core.gradients import gradient_table
from dipy.data import get_fnames
from dipy.io.gradients import read_bvals_bvecs
from dipy.io.image import load_nifti
from dipy.reconst.shore import ShoreModel
Download and get the data filenames for this tutorial.
img contains a nibabel Nifti1Image object (data) and gtab contains a GradientTable object (gradient information e.g. b-values). For example, to read the b-values it is possible to write print(gtab.bvals).
Load the raw diffusion data and the affine.
data, affine = load_nifti(fraw)
bvals, bvecs = read_bvals_bvecs(fbval, fbvec)
bvecs[1:] = bvecs[1:] / np.sqrt(np.sum(bvecs[1:] * bvecs[1:], axis=1))[:, None]
gtab = gradient_table(bvals, bvecs=bvecs)
print(f"data.shape {data.shape}")
data.shape (96, 96, 60, 203)
Instantiate the Model.
asm = ShoreModel(gtab)
Let’s just use only one slice only from the data.
dataslice = data[30:70, 20:80, data.shape[2] // 2]
Fit the signal with the model and calculate the SHORE coefficients.
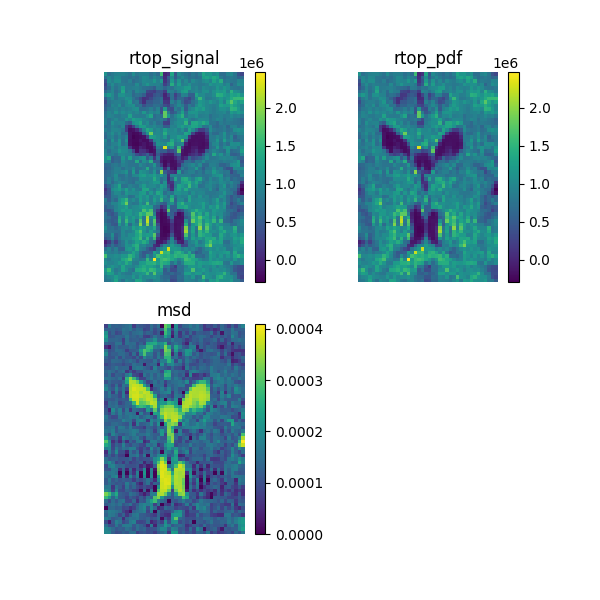
Calculate the analytical RTOP on the signal that corresponds to the integral of the signal.
print("Calculating... rtop_signal")
rtop_signal = asmfit.rtop_signal()
Calculating... rtop_signal
Now we calculate the analytical RTOP on the propagator, that corresponds to its central value.
print("Calculating... rtop_pdf")
rtop_pdf = asmfit.rtop_pdf()
Calculating... rtop_pdf
In theory, these two measures must be equal, to show that we calculate the mean square error on this two measures.
mse = np.sum((rtop_signal - rtop_pdf) ** 2) / rtop_signal.size
print(f"MSE = {mse:f}")
MSE = 0.000000
Let’s calculate the analytical mean square displacement on the propagator.
print("Calculating... msd")
msd = asmfit.msd()
Calculating... msd
Show the maps and save them to a file.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1, title="rtop_signal")
ax1.set_axis_off()
ind = ax1.imshow(rtop_signal.T, interpolation="nearest", origin="lower")
plt.colorbar(ind)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2, title="rtop_pdf")
ax2.set_axis_off()
ind = ax2.imshow(rtop_pdf.T, interpolation="nearest", origin="lower")
plt.colorbar(ind)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3, title="msd")
ax3.set_axis_off()
ind = ax3.imshow(msd.T, interpolation="nearest", origin="lower", vmin=0)
plt.colorbar(ind)
plt.savefig("SHORE_maps.png")
C:\Users\skoudoro\Devel\dipy\doc\examples_revamped\reconstruction\reconst_shore_metrics.py:86: RuntimeWarning: More than 20 figures have been opened. Figures created through the pyplot interface (`matplotlib.pyplot.figure`) are retained until explicitly closed and may consume too much memory. (To control this warning, see the rcParam `figure.max_open_warning`). Consider using `matplotlib.pyplot.close()`.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
RTOP and MSD calculated using the SHORE model.
References#
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.486 seconds)